- Jofa Tower 5th floor, SB-23, Block 13 C, Main University Rd, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi.
- +92 322 3746726
- tis@transformation.com.pk
Autism Causes and Treatment

Child Psychotherapy
May 24, 2023
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
June 14, 2023What is Autism?
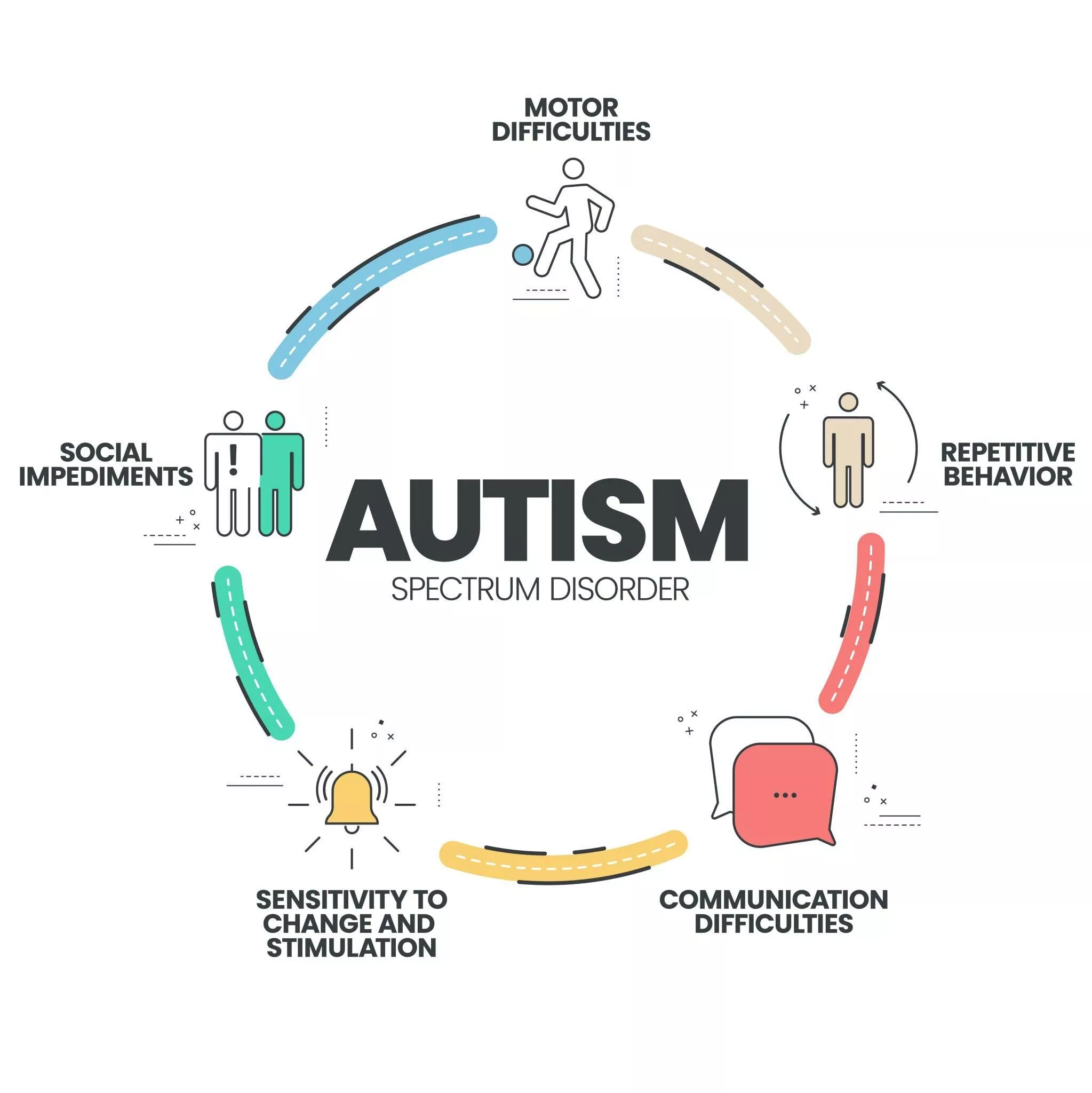
Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. It is called a spectrum disorder because the severity and symptoms of the disorder can vary widely from person to person. Symptoms of autism can be categorized into two main areas: social communication and restricted, repetitive behaviors. Some individuals with ASD may have difficulty with social interactions and communication, while others may have intense interests in certain subjects or may exhibit repetitive behaviors. The social communication symptoms include difficulty with eye contact, difficulty initiating or maintaining conversations, and difficulty understanding nonverbal communication such as facial expressions or body language. Whereas, restricted and repetitive behaviors may include repetitive motions such as hand flapping, a strong adherence to routines, and intense interests in specific subjects. The prevalence of autism has been increasing over the past few decades, with estimates suggesting that 350,000 children in the Pakistan have been diagnosed with ASD according to Pakistan Autism Society. Autism can be diagnosed as early as two years old, although it can be difficult to diagnose in some cases.
CAUSES OF AUTISM
The causes of autism are not entirely clear, but research suggests that genetics play a role. Studies have found that certain genetic mutations or deletions may increase the risk of developing ASD. Other factors that may contribute to the development of autism include prenatal exposure to environmental toxins, prematurity, and complications during childbirth. While the exact causes of autism are not fully understood, research has identified several factors that may contribute to the development of the disorder.
- Genetics: One of the most well-established causes of autism is genetics. Research has shown that certain genes or combinations of genes may increase the risk of developing autism. In fact, studies have found that if one identical twin has autism, there is a 70-90% chance that the other twin will also have the disorder. However, it is important to note that genetics alone do not explain all cases of autism.
- Environmental Factors: There are several environmental factors that have been linked to an increased risk of developing autism. These include:
- Prenatal exposure to certain toxins: Exposure to toxins such as lead, mercury, and pesticides during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of developing autism.
- Maternal illness during pregnancy: Maternal infections such as rubella, influenza, and cytomegalovirus have been linked to an increased risk of autism in offspring.
- Premature birth and low birth weight: Babies born prematurely or with low birth weight are at a higher risk of developing autism.
- Brain Development: Research has shown that abnormalities in brain development may contribute to the development of autism. Specifically, it is believed that disruptions in the formation or connectivity of brain cells may play a role. Studies have also found differences in the size and shape of certain brain structures in individuals with autism.
Other Factors: Other factors that may contribute to the development of autism include:
- Advanced parental age: Children born to older parents (especially fathers) may be at a higher risk of developing autism.
- Gender: Autism is more common in boys than girls, with boys being four times more likely to be diagnosed with the disorder.
Additionally, not all individuals with autism will have the same underlying causes. As research continues, it is hoped that a better understanding of the causes of autism will lead to improved diagnosis, treatment, and support for individuals with the disorder.
TREATMENT OF AUTISM
Treatment for autism typically involves a combination of behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and medication when necessary. While there is no cure for autism, there are several treatment options that can help individuals with the disorder manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Behavioral Therapy: Behavioral therapy is a type of treatment that focuses on changing specific behaviors that are causing problems for the individual with autism. This can include teaching social skills, communication skills, and self-care skills. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a specific type of behavioral therapy that has been shown to be effective for many individuals with autism. ABA uses a reward system to reinforce positive behaviors and discourage negative behaviors.
Speech Therapy: Many individuals with autism have difficulty with communication. Speech therapy can help these individuals learn language and communication skills. This can include teaching them to use words and gestures to communicate, as well as helping them understand nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and body language.
Medication: While there is no medication that can cure autism, medication can be helpful in managing certain symptoms of the disorder. For example, medication can be used to manage anxiety, depression, hyperactivity, and aggression. It is important to note that medication should always be used in conjunction with behavioral therapy and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Other Therapies: There are several other therapies that may be helpful for individuals with autism. These include:
Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy can help individuals with autism learn skills necessary for daily living, such as dressing and grooming themselves.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help individuals with autism improve their coordination and motor skills.
Sensory Integration Therapy: Sensory integration therapy can help individuals with autism learn to process sensory information such as touch, sound, and light.
The treatment for autism should be individualized based on the needs of the individual. There is no one-size-fits-all approach to treating autism, and what works for one individual may not work for another. Additionally, early intervention is key in improving outcomes for individuals with autism. The earlier treatment is started, the better the chances for success. Individuals with ASD have a wide range of abilities and strengths. While some individuals with ASD may struggle with social interaction, others may have exceptional abilities in areas such as math or music. With appropriate support and intervention, individuals with autism can lead fulfilling and productive lives.




