- Jofa Tower 5th floor, SB-23, Block 13 C, Main University Rd, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi.
- +92 322 3746726
- tis@transformation.com.pk
Autism in Childhood

Working Behind Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation(rTMS)
August 3, 2023
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS)therapy benefits
August 7, 2023Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disorder that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. It is called a spectrum disorder because the symptoms can vary widely in severity, ranging from mild to severe. The severe form of ASD is also called low-functioning autism and the mild form of ASD is also called high-functioning autism.
Autism treatment center in Karachi
The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition) is a widely used classification system for diagnosing mental disorders, including ASD. The DSM-5 TR (Text Revision) is a version of the DSM-5 that includes minor updates. The DSM-5 TR criteria for ASD are divided into two main areas i.e. social communication and restrictive/repetitive behaviors. To be diagnosed with ASD, a person must show symptoms in both of these domains. The criteria are as follows:
- Persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction:
- Deficits in social-emotional reciprocity (e.g., unusual social inhibitions like intrusive touching, difficulties with back-and-forth conversation, reduced sharing of interests or emotions, lack of initiative in interaction).
- Deficits in nonverbal communication (e.g., lack of eye contact, gestures, and facial expressions to communicate e.g. facing away from the listener, abnormal pitch and volume of speech).
- Deficits in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships (e.g., difficulties making friends, lacking interest in peers, difficulties in imaginative play).
- Restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities by at least two of the following symptoms:
- Stereotyped or repetitive motor movements, use of objects, or speech (e.g., hand-flapping, finger flicking, spinning coins lining up toys, echolalia)
- Insistence on sameness, inflexible adherence to routines, or ritualized patterns of verbal or nonverbal behavior (e.g., distress when routines are disrupted, adherence to rules, repetitive questioning, taking the same route or eating the same food every day, rigid thinking).
- Highly restricted, fixated interests that are abnormal in intensity or focus use (e.g. an intense interest in specific unusual topics and objects, a toddler strongly attached to a pan; a child preoccupied with vacuum cleaners; an adult spending hours writing out timetables).
- Hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input (e.g., heightened sensitivity to certain sounds, textures, or lights, excessive smelling or touching of objects, visual fascination with lights or movement, sometimes apparent indifference to pain, heat, or cold, extreme reaction to or rituals involving taste, smell, texture, or appearance of food or excessive food restrictions).
- The symptoms must be present in early childhood, even if they may not become fully apparent until later in life. Symptoms usually manifest during second year after birth but can be observed earlier in case of seropositive infant.
The symptoms should cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning e.g. insistence on routines and sensory sensitivity may trouble in eating, sleep and routine care like haircuts, dental work etc.
ASD is four times more common in males compared to females. Symptoms of ASD are universal meaning that symptoms remain the same across different cultural contexts. However cultural and socio-economic factors may affect the age at which diagnosis is made.
The exact cause of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is still not fully understood. Both environmental factors and biological factors including heredity may influence the development of Autism Spectrum Disorder. According to twin studies, when one member of the pair has ASD, the chances of the other member developing ASD ranges between 37% and more than 90%. Many genes are thought to contribute to the development of ASD, and certain genetic mutations or variations may increase the risk of developing the condition. Differences in brain structure and function have been observed in individuals with ASD. Disruptions in early brain development may play a role in the development of the disorder. Low socio-economic status, advanced parental age, low birth weight, exposure of a fetus to valproate (used to treat epilepsy, bipolar), and complications during pregnancy, may increase the risk of developing Autism Spectrum Disorder. Research in this field is ongoing, and there may be other factors that contribute to the development of ASD that have not yet been fully identified or understood.

Autism treatment center in Karachi

Symptoms are often most marked in early childhood and early school years, however, Autism Spectrum Disorder is not a degenerative disorder, and it is typical for learning and management to continue throughout life. It is important to remember that only a minority of individuals with ASD (individuals with lower levels of impairment, (high-functioning autism) live and work independently in adulthood. However, even these individuals may remain socially naive and vulnerable, and have difficulties organizing practical demands without aid.
Diagnosis is made by psychologists and psychiatrists. Accurate diagnosis requires information from a variety of resources including a detailed interview with parents or caregivers, clinical observation, use of standard psychometric measures like CARS (Children Autism Rating Scale), and an interview with a child if possible. Problems in social communication vary from child to child depending on the individual's age, intellectual level, and language ability, as well as other factors such as treatment history and current support.
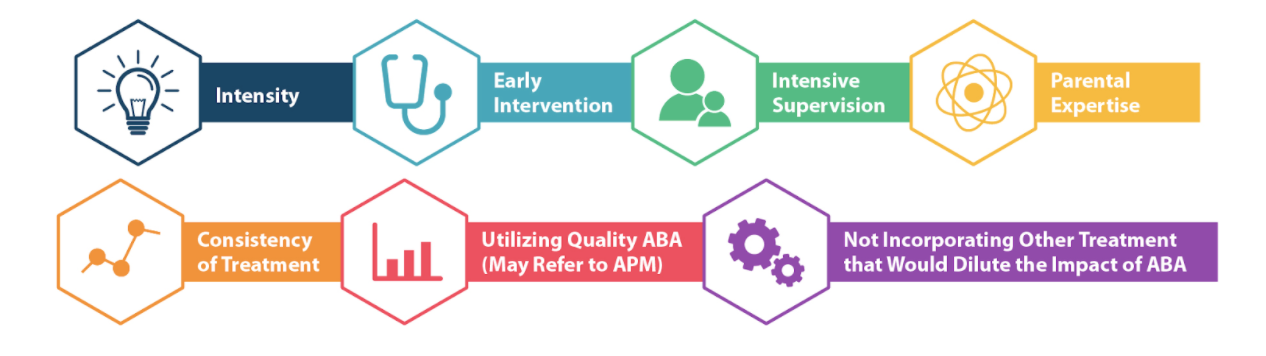
The treatment for ASD typically involves a multidisciplinary approach tailored to each individual's specific needs and challenges. Some common interventions include:
- Behavioral Interventions such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) and other behavior-based therapies can help individuals with ASD develop social and communication skills, reduce problematic behaviors, and promote positive behavior.
- Speech and language therapy to improve communication skills, language development, and pragmatic language use.
- Occupational therapy works on developing daily living skills, sensory integration, and fine motor skills.
- Social skills training These programs aim to enhance social interactions and improve the ability to understand and respond appropriately to social cues.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage certain symptoms associated with ASD, such as anxiety, hyperactivity, or aggression. However, medication is not a cure for ASD.
Raising a child with ASD can be emotionally daunting for parents. Counseling provides a safe space for parents to express their feelings, concerns, and frustrations, allowing them to process emotions effectively. Psychoeducation is very important when therapists provide parents with information about ASD, its characteristics, and its impact on their child's development. Understanding the disorder better can help parents become more effective advocates for their children and make informed decisions regarding treatment and interventions.




