- Jofa Tower 5th floor, SB-23, Block 13 C, Main University Rd, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi.
- +92 322 3746726
- tis@transformation.com.pk
Autism Symptoms in Children

Drug Rehabilitation Treatment
August 10, 2023
Best Treatment for Autism
August 11, 2023Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) stands as a multifaceted neurodevelopmental condition impacting communication, social engagement, and behavior. This intricate disorder exists along a spectrum, signifying that its presentation varies among individuals. Timely recognition and intervention play a pivotal role in aiding children with autism, facilitating their optimal growth. In this discourse, we shall explore prevalent signs of autism in children and offer perspectives on comprehending and managing these intricacies.
Autism treatment center in Karachi
Challenges in Communication:
Communication challenges stand out as a prominent feature of autism. Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often encounter difficulties when trying to initiate or sustain conversations. They may find it challenging to interpret non-verbal signals such as facial expressions and gestures. Additionally, there could be delays in their speech development. Some children with ASD might engage in echolalia, which involves repeating words or phrases they've heard. Conversely, while some may display remarkable language skills in specific areas like vocabulary or sentence structure, they might face struggles when it comes to grasping abstract language concepts and figurative expressions.
Recurring Patterns and Singular Passions:
The recurrence of patterns emerges as a distinctive hallmark in the context of autism. In children grappling with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), these patterns frequently manifest as repetitive actions such as hand-flapping or rocking. The adherence to consistent routines holds immense significance, and any deviation from these routines has the potential to evoke distress. Another noteworthy trait is the cultivation of intense passions revolving around specific subjects. These children may openly exhibit an exceptional enthusiasm for discussing or immersing themselves in these interests, often showcasing a unique inclination for intricate details.
Delayed Motor Skills:
Children with autism might experience delays in developing motor skills. This could manifest as challenges with coordination, balance, or fine motor skills such as handwriting. Some children may exhibit repetitive or unusual motor movements.
Timely Identification and Proactive Support:
The early recognition of autism symptoms holds paramount importance in facilitating meaningful intervention. Parents and caregivers assume a pivotal role in keenly observing and reporting any developmental indicators. Swift action through early interventions, encompassing speech therapy, occupational therapy, applied behavior analysis (ABA), and social skills training, can profoundly enhance the prospects and progress of children navigating the autism spectrum.
Social Interaction Challenges:
Children with autism often find social interactions challenging. They might struggle with making eye contact, sharing emotions, and understanding the emotions of others. They may have difficulty making and maintaining friendships, preferring to play alone or engaging in repetitive behaviors. Difficulty with perspective-taking and understanding social norms can contribute to misunderstandings and isolation.
Heightened Sensory Responses:
Heightened sensory responses are frequently observed in children diagnosed with autism. Certain sensory stimuli, like loud sounds, glaring lights, or specific textures, can trigger excessive sensitivity in these individuals. On the contrary, there are cases where some children actively seek out sensory input as a form of self-regulation, engaging in activities such as spinning or jumping to manage and balance their sensory experiences.
Unusual Play and Imagination:
Play and imaginative skills can also be affected in children with autism. They might engage in play that seems repetitive or lacks creativity. Pretend play might be limited or absent, and they might struggle with understanding imaginative scenarios.
Embracing Neurodiversity:
It is crucial to acknowledge that autism is an integral facet of the rich tapestry of human diversity. Every child with autism possesses distinct strengths and hurdles. Embracing the concept of neurodiversity entails recognizing and honoring these variations, nurturing an environment of inclusivity, and spotlighting each child's capacities, transcending a mere focus on their constraints.
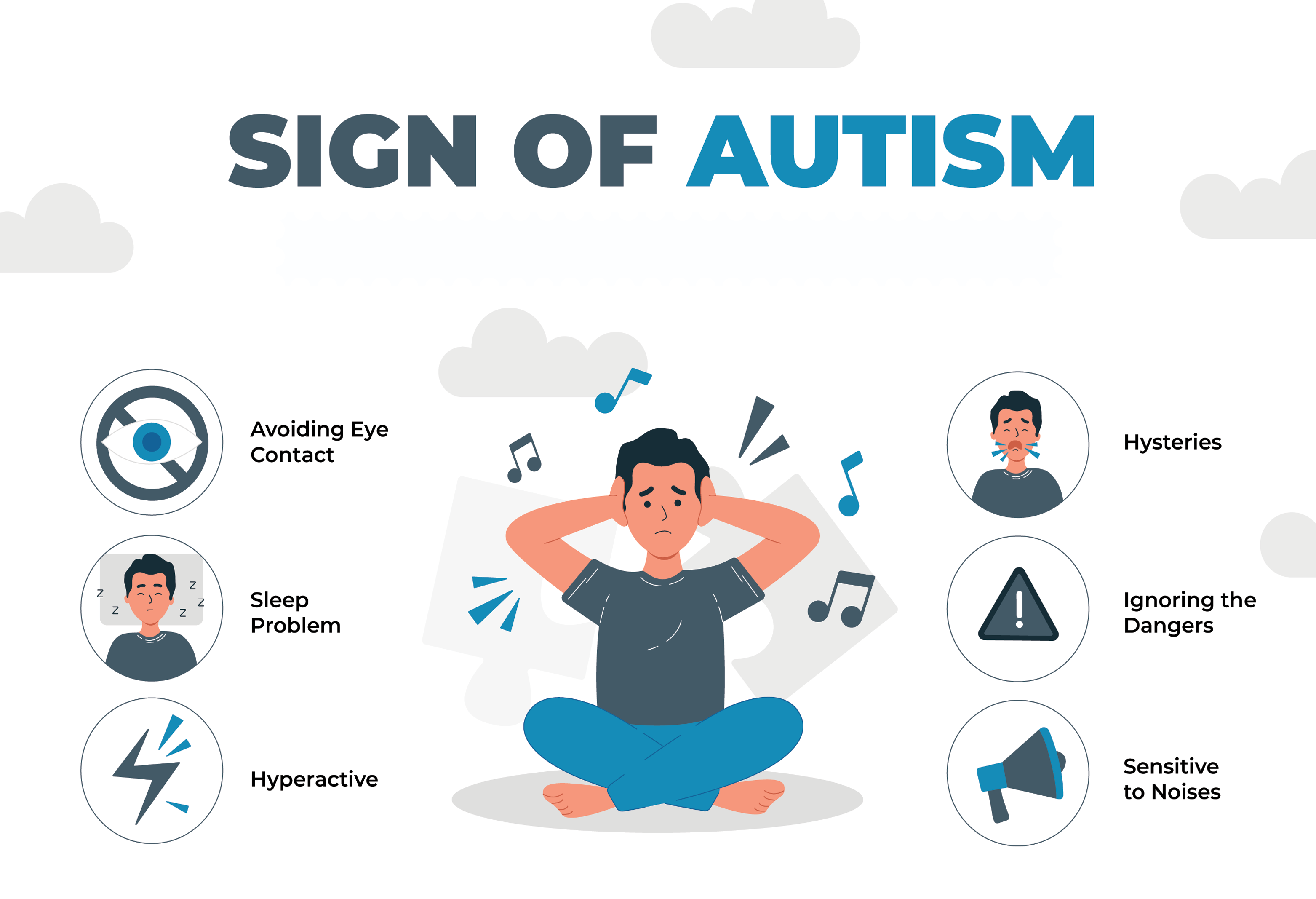
Guiding Steps for Addressing Autism Symptoms and Supporting Children's Well-Being:
Identifying signs of autism in a child requires prompt action to ensure early intervention and assistance. Timely detection and intervention have the potential to greatly enhance the child's developmental trajectory and overall quality of life. Here are the recommended steps to consider in such situations:
Seek Guidance from a Pediatrician or Healthcare Specialist:
Commence the process by seeking guidance from a pediatrician or healthcare specialist with expertise in child development. Their proficiency enables them to conduct a comprehensive evaluation and ascertain if the child's conduct and progress align with indications of autism symptoms or other developmental considerations.
Pursue a Comprehensive Developmental Evaluation:
If your child's healthcare provider expresses apprehensions regarding autism symptoms, they might recommend you to a specialist for a thorough developmental assessment. This evaluation could encompass a collaborative team of experts, including child psychologists, speech therapists, occupational therapists, and behavior analysts. Together, they will meticulously examine aspects like the child's communication, social engagement, behavior, and sensory processing.
Early Intervention Services:
If the assessment indicates a likelihood of autism or developmental delays, early intervention services should be initiated as soon as possible. Early intervention programs are designed to provide targeted therapies and support to address the specific needs of the child. These programs can include speech therapy, occupational therapy, behavior therapy (such as Applied Behavior Analysis), and social skills training.
Create a Supportive Environment:
As you await professional guidance and intervention, create a supportive and structured environment for your child. Establish routines, provide clear communication, and create sensory-friendly spaces to help your child feel secure and comfortable.
Connect with Support Networks:
Reach out to local autism support groups, online communities, and organizations dedicated to autism awareness and advocacy. Connecting with other parents and caregivers can provide valuable insights and emotional support.
Stand Up for Your Child's Needs:
Stand as a resolute champion for your child's necessities. Collaborate alongside healthcare professionals, educators, and therapists to formulate a personalized strategy that caters to your child's strengths and challenges.
Monitor Progress:
Regularly monitor your child's progress and adjust interventions as needed. Open communication with the child's intervention team is crucial for tracking development and making informed decisions.
Plan for the Future:
As your child grows, continue to plan for their educational and developmental needs. Explore educational options, including special education programs and inclusive classrooms, and work with professionals to set appropriate goals.




