- Jofa Tower 5th floor, SB-23, Block 13 C, Main University Rd, Gulshan-e-Iqbal, Karachi.
- +92 322 3746726
- tis@transformation.com.pk
Working Behind Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation(rTMS)

What is Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation?
August 2, 2023
Autism in Childhood
August 4, 2023In this article, we will explore the underlying mechanisms behind rTMS, including its foundational components and how it interacts with the human brain to influence neuronal activity.
The fundamental blocks of rTMS include
- Neurons - cells that make up the nervous system including the brain, spinal cords and nerves. There are billions and billions of neurons and their function is to transmit electrical impulses (carrying messages) forming a neuronal circuit.
- Magnetic coil - this specially designed coil is placed on the scalp and serves as a stimulator. When activated, this coil emits a brief but intense magnetic pulse that penetrates the scalp creating a magnetic field in the targeted brain structure which is crucial for the stimulation process.
- Electromagnetic induction - the magnetic field created by the stimulation of the coil induces small electrical currents in the underlying neural tissue, including neurons and their synapses.
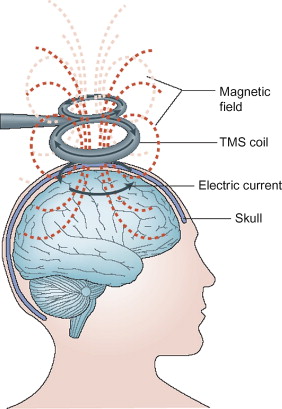
rTMS services in Karachi
Steps of the Working of rTMS:
- Screening: The patient is asked to get lab tests and other tests. He is further screened for the conditions that may contraindicate with rTMS treatment such as pregnancy, drug abuse, use of steroids, history of epilepsy, medical instruments implantation and other medical conditions that can get worse as a result of rTMS.
- Identifying targeted brain part: The first and foremost is to determine which part of the brain requires stimulation. This is done by a qualified and well-trained therapist based on the patient's complaints and symptoms. Neuroimaging techniques like MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), functional MRI (fMRI) or PET (Positron Emission Topography) scans can be utilized to pinpoint the optimal stimulation sites.
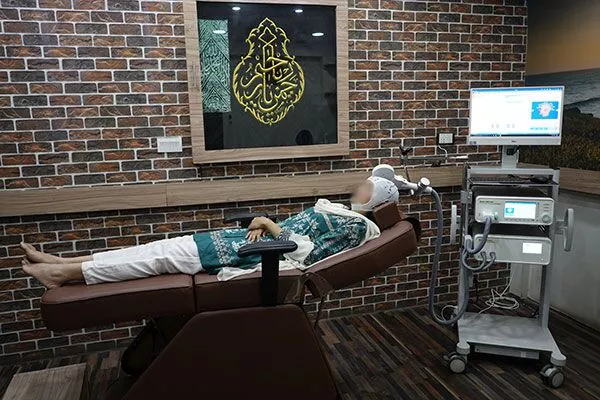
- Coil placement: The patient is seated comfortably on a recliner chair and asked to take off glasses with metal frames or remove any metallic jewelry items. Removing all metallic jewelry is a safety precaution in case they contain any magnetic metals. Earplugs are given to wear, that's because the sound of the magnet is loud enough to damage hearing. An electromagnetic coil is placed against the scalp over the targeted brain area. That either involves putting on the magnet-containing helmet (with a chin strap, so it stays in place) or positioning the extension arm with the magnet at its end, so the outer case of the magnet is against your face.
- Magnetic stimulation: The coil is stimulated to generate a magnetic pulse that transmits through the scalp and into the relevant brain region. This will cause tapping on the head and a loud clicking sound. The intensity of the magnetic pulses is adjusted to ensure that the stimulation is strong enough to penetrate the skull and reach the targeted brain regions, while still being within safe limits.
- Inducing electrical currents: As the magnetic pulse reaches the brain, it interacts with the neural tissue, particularly the neurons, releasing neurotransmitters in their synapses. This interaction leads to the induction of small electrical currents within the neurons. Magnetic stimulation can be excitatory or inhibitory depending upon the disorder being treated. Excitatory stimulation, created using high-frequency magnetic pulse i.e. 5 to 20 Hz, increases the rate of firing of neurons whereas inhibitory stimulation, carried out using low-frequency impulse which is typically 1 Hz, slows down the activity of neurons in the given brain region. Excitatory stimulation is usually given when the neurons are already slow e.g. depression.
- Polarization of Neurons: The induced currents can either depolarize or hyperpolarize the neurons' membrane potentials, depending on the stimulation parameters used.Simply put, hyperpolarization means that the inside of the neurons becomes more negatively charged compared to usual whereas depolarization means that inside of the neurons become positively charged. During hyperpolarization, the neuron is idle meaning electric impulse is not transmitted whereas the depolarization phase causes neurons to fire to transmit impulses. When depolarization is the goal, excitatory stimulation is given. Inhibitory stimulation is used to achieve hyperpolarization in the targeted brain area.
- Modulating neuronal activity: The induced electrical currents effectively influence the firing patterns of neurons in the stimulated region. Repeated sessions of rTMS can lead to long-lasting changes in neuronal excitability, connectivity, and neurotransmitter release. This neuroplasticity is believed to be a key mechanism through which rTMS exerts its therapeutic effects.
- Duration of session: The duration of each rTMS session can vary based on the treatment protocol and the patient's needs. A typical session usually lasts between 20 to 30 minutes.
- At the end of the session: Common side effects of rTMS are usually mild and transient, including headaches, scalp discomfort, light-headedness during or after the session, and mild facial muscle contractions. Symptoms like headaches and lightheadedness usually go away afterward.
- Number of sessions: The number of rTMS sessions required for an effective treatment course varies depending on the condition being treated and individual patient responses. A standard treatment course may consist of multiple sessions conducted over several weeks.

Comparison between rTMS and EEG:
The effectiveness of rTMS varies depending on the condition being treated, the targeted brain region, and individual patient factors. For some patients, rTMS can produce significant improvements, while for others, the effects may be more modest. It is crucial to note that rTMS are generally considered safe, especially when compared to invasive brain stimulation methods e.g. EEG (electroencephalogram). In EEG, the patient is given anesthesia so that person becomes unaware of the surroundings and muscle relaxants. This has side effects as the chemical is being given and requires monitoring whether anesthesia can be given or not. Besides EEG targets the entire brain while rTMS is applied to only the targeted brain region. Clearly, this makes rTMS less threatening compared to EEG.
Conclusion:
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) is an advanced neuromodulation technique that utilizes magnetic fields to influence brain activity. By employing electromagnetic induction, rTMS can stimulate or inhibit targeted brain regions, leading to changes in neural excitability and connectivity. This non-invasive procedure holds tremendous promise in treating various neurological and psychiatric conditions, providing hope to patients who haven't found relief with traditional therapies. As research and technology continue to advance, rTMS is likely to play an increasingly prominent role in the ever-evolving landscape of brain health and medical interventions.




